ABOUT THE GFCF DIET
What is the Gluten and Casein Free Diet?
The gluten and casein free (GFCF) diet is a diet in which all foods containing gluten and casein are fully eliminated from a person’s daily food intake. The GFCF diet was specifically created for people who suffer from a gluten and/or casein intolerance. While some people are known to experience less serious physical effects after the consumption of gluten and casein, like gastrointestinal implications such as diarrhea, constipation, bloating, or vomiting, there are others who experience more serious implications, that are not only physical, but psychological as well. Some of these effects are caused by allergic reactions to gluten and casein, and others are due to conditions such as Celiac disease, which is an autoimmune disease, or leaky gut syndrome, which is a condition related to the intestines. Although the GFCF diet is very popular amongst those who suffer from conditions such as these, there are many parents and professionals who believe that a GFCF diet may help to improve the symptoms in children with autism or have been diagnosed under the autism spectrum. Although there is no scientific evidence that proves this to be true, there are many people who support this belief due to the fact that so many children diagnosed under the autism spectrum have also been documented has having allergic reactions to gluten and casein, autoimmune ailments, gastrointestinal problems, Celiac disease, and leaky gut syndrome.
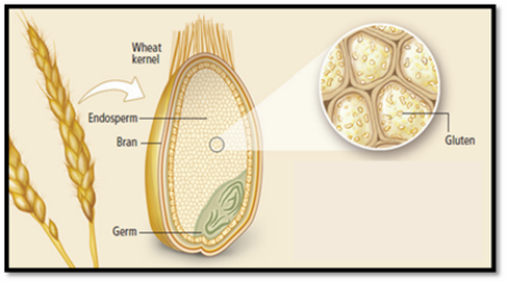
What is Gluten and Where Can it Be Found?
According toThe American Heritage Dictionary of the English Language, gluten is defined as follows: 1."The mixture of proteins, including gliadins and glutelins, found in wheat grains, which are not soluble in water and which give wheat dough its elastic texture. 2. Any of the prolamins [proteins] found in cereal grains, especially the prolamins in wheat, rye, barley, and possibly oats, that cause digestive disorders such as Celiac disease"(Gluten). There are many foods that contain gluten proteins, but the most common of these foods are cereals, breads, crackers, pastas, and other carbohydrates. While gluten is most commonly found in foods, it can also be found in other unsuspected sources such as vitamins, supplements, medications, and cosmetics, so it is important for those people who are trying to avoid gluten to check product labels to ensure they are not accidentally consuming gluten.
What Is Casein and Where Can It Be Found?
Casein, also sometimes referred to as “caseinogen,” is a protein that is found in milk, and is “part of a group called phosphoproteins, collections of proteins bound to something containing phosphoric acid” (What is Casein?). There are two types of casein, which include “edible” casein and “technical” casein. Edible casein is found in foods containing dairy, but it is also used in medicines and processed foods, “both for nutritional value and as a binder” (What is Casein?). “Technical” casein is used in everything from cosmetics, nail polishes, paints, plastics, and more. It is important for those people who are trying to avoid casein to know that they may still experience a reaction to casein even after eliminating it from their diet, especially if they are using products that contain casein. Also, they should know that even though a product may be labeled as being lactose free, there is still a possibility that it can contain casein.
Can Gluten and Casein Be Harmful to Anyone?
Typically, gluten and casein are not known to cause harm to the majority of people. In fact, many foods containg gluten and casein are known as being very high in vitamins and nutrients; however, research suggests that some people believe there is a possible link between casein and cancer, but this is still being researched and therefore has never been proven. The only time that gluten and casein are noted as being harmful to a person is if the person suffers from allergies or intolerance to gluten and or casein. This is because when a person suffers from a gluten allergy or intolerance, their bodies are unable to properly digest foods containing these specific proteins. The undigested proteins are known as peptides, which can be toxic once they enter the blood; thus, triggering a reaction in the immune system, or gastrointestinal implications.